MLN Diagnostic Tools & Techniques
Diagnostics for MLN are focused on the individual causal viruses. In East Africa, MCMV is considered the primary target for the diagnostic tools. A range of different diagnostic options exist for the detection of MLN causal viruses e.g., MCMV. The primary diagnostic techniques include:
- ELISA
- Immunostrips
- LAMP
- PCR
Choice of MLN diagnostic technique is influenced by cost, availability of specialized equipment and trained personnel, and purpose of the study. A combination of methods is often needed if absolute confirmation or detailed analysis is required. The following table gives a summary of the main MLN diagnostic techniques:
Comparison of MLN Pathogen Diagnostic Techniques
| TECHNIQUE | ASSESSMENT | REPRODUCIBLITY | TIME | LABOR | COST/SAMPLE |
| ELISA | VIRAL ANTIGEN | GOOD | HOURS | MODERATE | MODERATE-HIGH |
| IMMUNOSTRIPS | VIRAL ANTIGEN | GOOD | LESS THAN 30 MINUTES | MODERATE | MODERATE-HIGH |
| Loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) | VIRAL GENE | EXCELLENT | HOURS | LOW, EXPERIENCED | MODERATE-HIGH |
| PCR | VIRAL GENE | EXCELLENT | HOURS | HIGH, EXPERIENCED | HIGH |
For large-scale, cost-effective regional diagnostics in East / Southern Africa CIMMYT and national partners are focusing on field-based immunostrips (leaf samples) and ELISA (confirmation assays and seed samples).
Full details of different diagnostic techniques can be found in:
- CIMMYT Brochure on MLN Diagnosis
- CIMMYT MLN protocols manual.
An overview of immunostrips and ELISA are given below.
Immunostrips
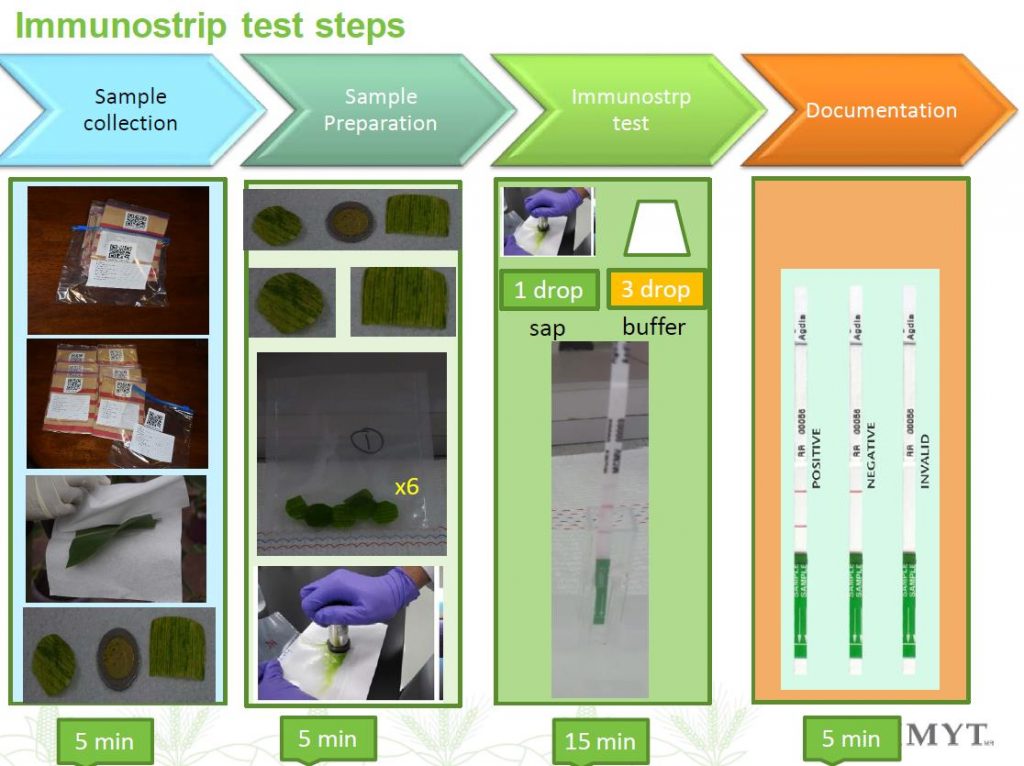
Several commercial immunostrip kits are available which are virus-specific e.g., for MCMV. The immunostrip kits are used on homgenized leaf tissue in the field. The advantage of these kits are that they are simple to use (no specialist knowledge required), give a rapid in-field result, stable in a wide range of climates and relatively inexpensive. The principle of the test is based on capillary flow of plant sap across a control strip (captures all molecules to ensure that reaction and strip working) and a viral specific antibody strip (captures only the specific virus molecules). The result is an easy to read pattern of bands (single band for negative, double-band for positive). An overview of the immunostrip assay on leaf tissue is given in the figure below.
ELISA
ELISA is probably the most popular method for detecting viruses in plant material, insect vectors, and seed. ELISA can be used to test a large number of samples in a short time due to its simplicity, adaptability, sensitivity and economy in the use of reagents. ELISA assays are based on the ability of the antibody to recognize and bind to a specific antigen (a substance associated with the pathogen). Several commercial companies produce high quality ELISA kits for all MLN-causing viruses. Most commercially available ELISA kits for detecting SCMV and MCMV use the double antibody sandwich (DAS) ELISA technique.
Important points to consider when using an ELISA assay:
- Always follow the kit manufacturer’s instructions precisely
- Always include both positive and negative controls – both form the manufacturer and also local controls
- Ensure carful sample preparation (either seed or leaf material), paying attention to maintain the correct sample to buffer ratio
- Careful interpretation of results using either visual interpretation or use of spectrophotometer.
An overview of the main of the main steps in an ELISA protocol are given in the figure below.

Source: CIMMYT MLN Pathogen Diagnosis, MLN-free Seed Production and Safe Exchange to Non-Endemic Countries
For more information on MLN Diagnostics please contact:
Dr. Suresh, L.M. | Maize Pathologist – Sub Saharan Africa, Global Maize Program &
Manager – MLN Screening facility
International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT)
World Agroforestry Centre (ICRAF), United Nations Avenue, Gigiri. P.O.Box 1041–00621, Nairobi, Kenya
tel: +254 (20) 7224069 skype: suresh.lm cel: +254 702392664 Tweeter : _lmsuresh
